Rendering
The Rendering panel provides a quick access to the Render Document Properties.
This Panel is divided into the following sections:
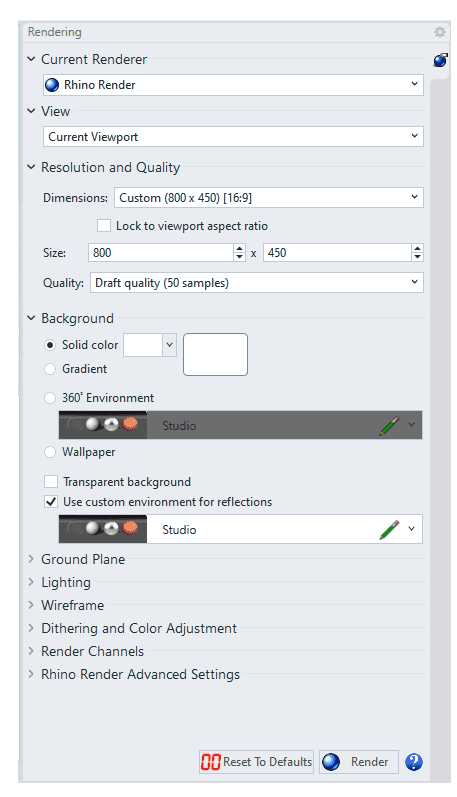
1. Current render
Sets the current renderer. This can be the built-in Rhino Render or a plug-in.
2. View
Specify a source for the view.
- Current Viewport: Renders the current viewport.
- Specific Viewport: Select a viewport to render from the list.
- Named View: Select a named view to render from the list.
- Snapshot: Select a snapshot to render from the list.
3. Resolution and Quality
Dimension
The aspect ratio displays to the right of the menu.
- Viewport(size): Renders the active viewport the active viewport using the pixel size of the viewport.
- Custom(size): Renders the active viewport using the custom resolution. Type the custom width and height resolution in pixels.
- Preset sizes: Renders the active viewport the selected pixel resolution.
Lock to viewport aspect ratio
Maintains the aspect ratio of the viewport. When the height or width is changed, the other dimension changes in relation.
Size
Calculates the size of the image in the selected unit system based on the Resolution and DPI ("dots" per inch) settings. This is useful for determining the size of the image for printing.
Quality
Selects the render quality based on number of samples used.
Opting for higher values will enhance the quality with an increase in rendering time.
- Low quality: Render 15 samples.
- Draft quality: Render 50 samples.
- Good quality: Render 500 samples.
- Final quality: Render 1500 samples.
4. Background
The Background defines what you see directly in front of the camera if there are no objects in the way. The background is not 3D, it exists only on the screen.
- Solid color: Displays a solid color. Click the color swatch.
- Gradient: Displays a two-color gradient. The color for the top of the image background is the Solid color set above.
- 360° Environment:
Displays the portion of the current environment that the camera sees in the viewport.  New
New
Creates a new environment using a template from the library. Edit
Edit
Edits the selected environment. Duplicate
Duplicate
Copies the selected environment to a new environment with the same settings.- Wallpaper: Displays the current viewport wallpaper.
Stretch to fit
Fits the wallpaper to the rendered view.
Transparent background
The background is rendered with an alpha channel for transparency. The image must be saved to a file format that supports alpha channel transparency (.png, .tga, .tif).
Use custom environment for reflections
Assigns a custom environment that will be reflected by objects in the scene.
5. Ground Plane
The Ground plane provides an infinite horizontal platform for the image that stretches to the horizon in all directions positioned at a defined elevation.
A ground plane renders much faster than using a surface as a background. Any material can be assigned to the ground plane.
More settings
Opens the Ground Plane panel.
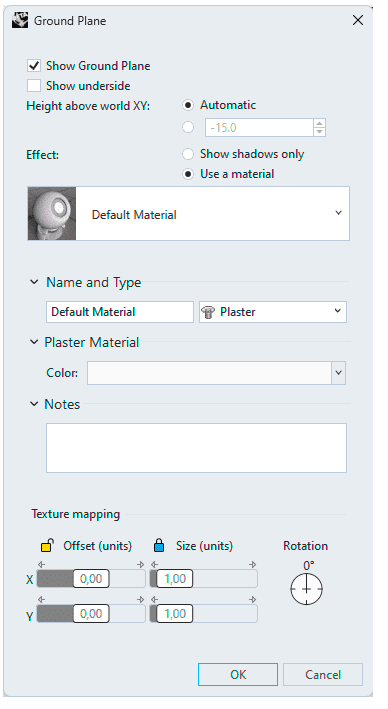
On
Turns on the ground plane.
Show underside
Allows the "back" of the ground plane to be visible when viewed from below. Otherwise, the underside is transparent
Height above world XY plane
Sets the ground plane's height above the xy plane.
- Automatic: Turns on auto-elevation that moves Ground Plane to the lowest point of the objects in the model. New objects added to the scene may change Ground Plane elevation.
Effect
- Shadow only: Makes the ground plane transparent, but allows shadows to still be cast on it.
- Use a material: Assigns a material to the ground plane and edits the material. See Materials.
- Texture mapping
These settings apply when a texture applied to the ground plane. - X/Y Offset (units): Specifies the offset distance in units from 0,0,0.
- X/Y Size (units): Specifies the size in units of the texture.
- Rotation: Specifies the rotation angle of the texture from 0.
6. Lighting
Sun
Turns on the sun.
- Sun Settings
Opens the sun panel.
Skylight
Turns on skylight.
- Intensity
Adjusts the skylight intensity. - Use custom environment for skylighting
Sets an environment that is used as sky light.
Lights
Opens the Lights panel.
Use lights on layers that are off
Controls whether or not spotlights that are on hidden layers or that are hidden with the Hide command are rendered.
7. Wireframe
Render curves
Curve objects are rendered with the surfaces.
Render surface edges and isocurves
Surface isoparametric curves and edges are rendered with the surfaces. Edge thickness set in the Rendered viewport apply.
Render points and point cloud
Points and point clouds are rendered with the surfaces.
Render dimensions and text
Dimensions and texts are rendered with the surfaces.
8. Dithering and Color Adjustment
Dithering
The rendered image is usually produced at a higher color depth than monitors and low-dynamic-range file types like bitmaps like JPEG, PNG, BMP can reproduce.
The most important effect this causes is banding, which is a quantization error. Dithering reduces quantization errors and so gets rid of banding.
Both dithering methods, generally do the same thing. Sometimes, one might be better than the other, but in general, Simple Noise is the best.
See: Wikipedia: Dither.
- None: No dithering.
- Floyd-Steinberg: The algorithm achieves dithering by diffusing the quantization error of a pixel to its neighboring pixels
- Simple noise: A random variation of brightness or color information in images.
Gamma
Image files are color corrected so that they can be loaded byte-by-byte into the RGB pixels of a computer screen and look right on a monitor. This means that the color response of a standard image is non-linear, that is, it is gamma corrected.
Gamma refers to the power function that is used to correct the image.
The Gamma value changes, and therefore corrects the output of the image.
See: Wikipedia: Gamma correction.
- Use linear workflow
The Rendered display mode supports a linear workflow for accurate color, gamma and lighting computation.
Gamma correction for bitmap images that are loaded from disk is removed (by the inverse of the amount in the Gamma edit box) so that they have a linear response before they are passed to the renderer.
The renderer renders them in this uncorrected state. The gamma correction is applied to the entire finished image. This can do a better job of processing the color in rendered images.
9. Render Channels
Automatic
Automatically enables the required render channels.
Custom
Manually select the render channels to include in the rendering.
- RGBA
Represents Red, Green, Blue, and Alpha transparency. It is mainly used for presentations. - Distance
Uses grayscale colors to represent the distance from the camera. The farthest pixel in the rendering is black. The nearest pixel is white. - Normal
Uses RGB values to represent the XYZ coordinates of normal directions. Red=X, Green=Y, and Blue=Z. - Albedo
The unshaded colors. It is the result of rendering a scene with totally uniform lighting and without shadows.
10. Advanced Rhino Render Settings
Seed
Change the seed value to vary the noise pattern.
Session
- Samples
Amount of samples taken per pixel in the Raytraced viewport. More samples means better convergence, thus better quality. - Override Production Render Quality
When enabled, the Render command will use the samples above to render the scene. Render quality settings will be ignored.
Ray Bounces
- Maximum bounces
Maximum number of light bounces. For best quality, this should be set to a high value. However, in practice, it may be good to set it to lower values for faster rendering. Setting the maximum to 0 bounces results in direct lighting only. - Diffuse
Maximum number of diffuse bounces. The ray is generated by a diffuse reflection or transmission (translucency). - Glossy
Maximum number of glossy bounces. The ray is generated by a glossy specular reflection or transmission. - Transmission
Maximum number of transmission (light that is transmitted throughout a volume) bounces. - Volume
Maximum number of volume scattering bounces. - Transparency
Maximum number of transparency bounces.
Texture Baking
When decal textures, multi-channel textures, procedural textures, or textures using custom mappings are rendered by Rhino Render or in the Raytraced viewport, these texture types are converted into bitmap textures.
Baking qualities control the bitmap texture resolution:
- Low: 2048 x 2048 pixels
- Standard: 4096 x 4096 pixels
- High: 8192 x 8192 pixels
- Ultra: 16384 x 16394 pixels
When you zoom in close to an object, the types of textures may look pixelated in the rendering if the baking quality is less than required. Using a higher baking quality will fix the problem, but memory usage of the rendering will increase exponentially.
![]() Reset To Defaults
Reset To Defaults
Restores all default rendering settings.
![]() Reset To Defaults
Reset To Defaults
Restores all default rendering settings.